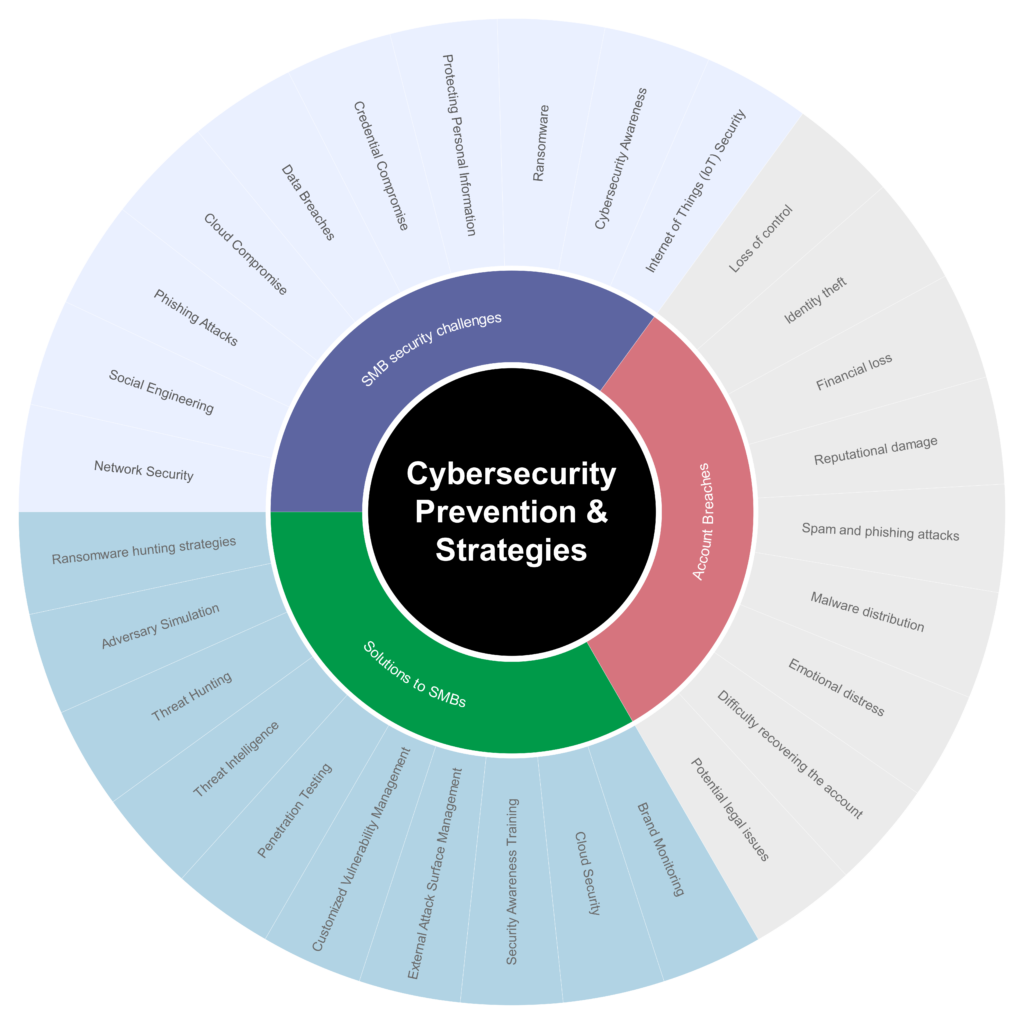
Cybersecurity Prevention & Strategies
Cybersecurity is a never-ending battle, but with a layered approach that combines prevention and mitigation strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks. Here’s a Cybersecurity Prevention & Strategies:
1. SMB (Small and Medium-Sized Businesses) security challenges:
Network Security
- Limited Resources: Unlike larger companies, SMBs sometimes have smaller IT teams and tighter budgets. This might make it challenging to engage specialized cybersecurity experts, purchase cutting-edge security solutions, and stay up to date with the constantly changing threat landscape.
- Misconfigured Systems: Inexperienced individuals may misconfigure security software, making it ineffectual. Vulnerabilities that attackers can take advantage of include weak firewall rules, unpatched vulnerabilities on systems, and unsafe cloud storage configurations.
- Weak Passwords and BYOD: Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) might permit consumers to use their own devices to access the network (BYOD) or have liberal password restrictions. If hackers can dupe staff members into falling for phishing schemes or take advantage of weaknesses on unprotected devices, this opens up easy access points for them.
- Unmonitored Network behavior: SMBs may be unaware of questionable behavior on their network if they lack the necessary monitoring technologies. Attackers may be able to move covertly laterally within the network as a result.
Social Engineering
Social engineering presents a major hurdle for SMBs in the realm of cybersecurity. The Reasons SMBs Are Vulnerable
- Limited resources: SMBs frequently do not have the funds to install a strong security infrastructure or engage specialized cybersecurity personnel.
- Focus on growth: Businesses first give income generation precedence over cybersecurity precautions.
Lack of awareness training: Staff members may not be able to identify and resist social engineering attempts.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a major concern for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) due to a few key factors:
- Limited Resources: In comparison to larger companies, SMBs may have fewer IT teams and budgets. This might make it challenging to put strong security measures in place and educate staff members about online dangers like phishing.
- Employee Education: Human error is a common target for cyberattacks. Employees at SMBs with limited resources could find it difficult to receive regular and efficient cybersecurity awareness training.
- Trust Factor: Phishers frequently pose as reliable sources, such as partners, suppliers, or even coworkers, to target SMBs. Employees may be more vulnerable to a deceptively written email that looks to be from a familiar person in a smaller work setting.
Cloud Compromise
SMBs have benefited greatly from cloud adoption because it offers scalability and cost-effectiveness. However, it also presents fresh security difficulties. Particularly damaging can be a cloud compromise, in which an attacker obtains unauthorized access to a small and medium-sized business’s cloud storage or service. For SMBs, cloud compromise is a big worry for the following reasons:
- Misconfigured Systems: SMBs frequently do not have the funds to invest in comprehensive cloud security.
- Weak Credentials: A lot of SMBs utilize the same passwords for several platforms or depend on weak passwords.
- Increased Attack Surface: Attackers can target vulnerabilities anywhere in the cloud environment, that do not require physical access to servers.
- Restricted Visibility: SMBs could find it difficult to keep a full picture of their cloud infrastructure. This makes it challenging to identify compromised systems or notice questionable activity.
Data Breaches
Small and medium-sized businesses are unfortunately prime targets for cyberattacks, including data breaches. They often have weaker cybersecurity defenses compared to large enterprises, making them easier targets for attackers. Hackers know this and specifically target SMBs.
Credential Compromise
An SMB may suffer greatly from a successful credential compromise, including:
- Data breaches: Sensitive information, such as financial records, customer information, or intellectual property, can be taken by hackers.
- Financial Loss: SMBs could have to foot the bill for fines, credit monitoring for impacted clients, and data recovery.
- Disruptions: A cyberattack may cause operational disruptions for businesses, resulting in lower output and income.
Reputational Damage: An SMB’s reputation may be severely harmed by a data breach, which could result in a loss of clientele.
Protecting Personal Information
SMBs, or small and medium-sized organizations, encounter particular difficulties in protecting personal data. Below is a summary of some of the main obstacles they face:
- Limitations on Resources
- Knowledge of Security
- Technical Difficulties
Ransomware
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are more susceptible to ransomware attacks, in which a company’s data is encrypted by malicious software and held hostage until a ransom is paid. For SMBs, these attacks may have dire repercussions, such as monetary loss, lost revenue, business interruption, harm to their reputation, and possible legal problems.
Cybersecurity Awareness
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are prime targets for cyberattacks, despite often lacking the resources of larger corporations. One of the biggest challenges for SMB cybersecurity is cybersecurity awareness. This means educating employees about cyber threats and how to avoid them.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) brings a wave of benefits for SMBs, from automation and efficiency gains to improved monitoring and security. However, these connected devices also introduce new security challenges that SMBs need to be aware of. Here’s a breakdown of the main issues:
- Weaknesses in Device Security
- Lack of Visibility and Control
- Increased Attack Surface
2. Account Breaches
Loss of control
Account breaches result in the loss of control over private data, which puts both people and businesses in danger. Numerous things, such as malware infections, phishing scam susceptibility, weak passwords, the absence of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and public data breaches, can cause these breaches.
Identity theft
Account breaches and identity theft are unfortunately linked. An account breach is when a hacker gains access to a database that stores personal information. This information can include names, addresses, Social Security numbers, credit card numbers, and even medical records. If this information falls into the wrong hands, it can be used for identity theft.
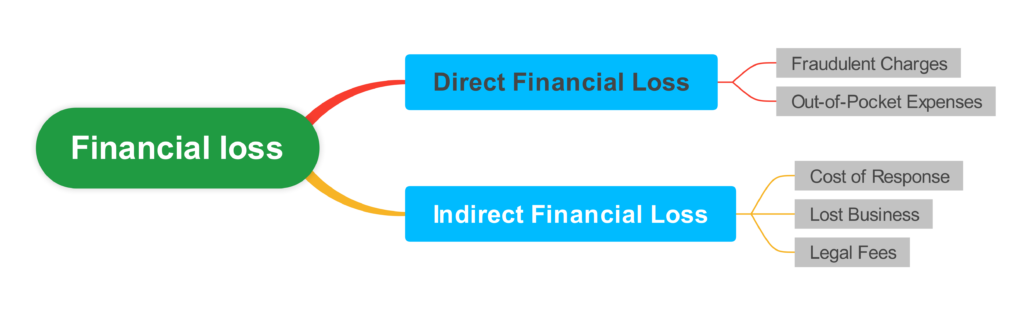
Financial loss
Both people and businesses may suffer large financial losses as a result of account breaches. Below is a summary of the various ways in which these losses may happen:
- Direct Financial Loss
- Indirect Financial Loss
Reputational Damage
In the context of cybersecurity, reputational damage is the term used to describe the harm that a cybersecurity incident, like a data breach, does to a company’s image. In addition to interfering with corporate operations, the exposure of sensitive customer data seriously damages consumer confidence. This breakdown of trust may result in lost business, a decline in sales, and permanent damage to the company’s brand.
Spam and phishing Attacks
spam and phishing attacks are major culprits behind account breaches. these attacks are two prevalent forms of cyber threats that target users through digital communication channels, primarily email. Both pose significant security risks, but they operate with slightly different objectives and mechanisms. Understanding these threats is crucial for individuals and organizations alike to develop effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
Malware distribution
Malware distribution and account breaches are two sides of the same coin. Account breaches are a common means by which hackers propagate malware and extend their access to compromised data and systems.
Emotional distress
Emotional distress resulting from account breaches is a significant concern, impacting victims’ mental well-being in various ways. Individuals affected by data breaches often experience a range of negative emotions, including anger, annoyance, frustration, upset, and a sense of betrayal.
Difficulty recovering the account
Various factors may affect the difficulty of recovering an account, such as the type of breach, the security protocols implemented, and the service provider’s response. The following are some difficulties people may run across while they are recovering:
- Identifying the Breach
- Regaining Access
- Verifying Identity
- Dealing with Consequences
- Preventing Future Breaches
Potential Legal Issues
Companies may run into several possible legal problems that call for quick decision-making.
3. Solutions to SMBs
Brand Monitoring
The act of regularly monitoring internet references of your company, its goods, or its rivals is known as brand monitoring. It gives you the ability to see what others are saying about you and is similar to having your ear on the ground in the digital realm.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/brand-abuse-monitoring/
Cloud Security
Cloud security services encompass a wide range of tools and technologies designed to safeguard data, applications, and infrastructure residing in the cloud environment.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/cloud-security-strategy-service/
Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training is crucial for any organization, especially in today’s digital landscape. It equips employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and respond to cyber threats, ultimately minimizing human error as a security risk.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/cybersecurity-awareness-training/
External Attack Surface Management
External Attack Surface Management (EASM) services help organizations identify and manage the security risks associated with their internet-facing assets.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/external-attack-surface-management/
Customized Vulnerability Management
Customized vulnerability management takes a one-size-fits-all approach to vulnerability scanning and replaces it with a strategy tailored to your organization’s specific needs.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/customized-vulnerability-assessment/
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, often shortened to pen testing, is essentially a simulated cyber attack on your computer systems or networks. It’s conducted by ethical hackers, security professionals who use their skills to identify vulnerabilities that malicious actors might exploit.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/penetration-testing-and-red-teaming/
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is essentially the gathering and analysis of information about potential and existing cyber threats. It’s like having a detective on your cybersecurity team, constantly investigating and providing insights to proactively defend your systems.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/threat-intelligence/
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting is the proactive process of searching for hidden threats within a network or system. Unlike traditional security measures that rely on reacting to alerts, threat hunting takes an aggressive stance to identify and isolate malicious activity before it can cause damage.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/cyber-threat-hunting/
Adversary Simulation
Adversary simulation, also known as adversary emulation, is a cybersecurity exercise designed to test an organization’s defenses against real-world cyber threats.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/adversary-simulation/
Ransomware hunting strategies
Ransomware hunting is the proactive process of searching for signs of ransomware infection within a network before it encrypts data or disrupts operations.
Visit: https://threatactix.com/services/ransomware-hunting-and-prevention-strategies/